Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine are a kind of human remuneration for standing walking. It is known that other mammals do not suffer from osteochondrosis because their spine is located horizontally with respect to the surface of the earth. Vertical loads when walking lead to the gradual destruction of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs and contribute to the displacement of the vertebrae into a dangerous position.

In the thoracic region, such processes occur less often than in the sacral and cervical regions, but this does not decrease the danger of this disease. This article will discuss in detail the symptoms and treatment issues of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, as well as elements related to the prevention of this disease.
Characteristics of thoracic osteochondrosis
The thoracic spine is characterized by low mobility, which reduces the likelihood of degenerative processes in this area. Nevertheless, cases of this disease are regularly recorded by orthopedists and traumatologists in representatives of different age groups.
In recent decades, there has been a steady increase in the incidence of osteochondrosis in civilized countries. Doctors believe that the main reasons for this trend are an inactive lifestyle, poor diet, and the general environmental context of the planet.
Women have chest osteochondrosis 2-3 times more often than men. This is due to the peculiarities of female anatomy and physiology. The additional influencing factors are: childbirth, walking in heels, general weakness of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus in women.
In both sexes, osteochondrosis of the thoracic region causes painful symptoms and reduces range of motion. The progression of pathology is fraught with compression of nerve endings, which inevitably affects the condition of internal organs. Advanced cases of the disease are often accompanied by disturbances in the work of blood vessels and heart, respiratory problems.
Anatomically, 12 thoracic vertebrae connect with the ribs and the breastbone in a strong, inactive skeletal structure that protects internal organs from mechanical stress. At the initial stage, the disease almost does not cause severe symptoms, but in the later stages the manifestations of pathology are so diverse that sometimes it prevents an accurate diagnosis. It's no wonder that osteochondrosis is often referred to as “chameleon disease”.
The most common causes of thoracic osteochondrosis are trauma, muscle weakness, physical inactivity, metabolic disturbances, excessive back strain and genetic predisposition. The disease develops gradually, which, on the one hand, makes it possible to start treatment in time and stop degenerative processes, but on the other hand, it prevents the early detection of the pathology.
Stages of the disease
Doctors classify thoracic osteochondrosis by stages of development:
Step 1.The intervertebral discs lose their elastic qualities, decrease in size, but do not yet move from their anatomical position.
Step 2.There is a further decrease in the height of the discs, and the spine itself loses its stability. Cracks form in the ring, the discs move and put pressure on nerve endings, blood vessels and muscles. The second stage is characterized by severe back pain and neurological symptoms.
Step 3.Degenerative processes can lead to the development of protrusions and ruptures of the fibrous ring. In such cases, herniated discs are diagnosed. The discs lose their cushioning properties and cease to perform their proper anatomical functions. The vertebrae themselves also suffer - they come together, collapse and form osteophytes - dangerous bone growths.
In addition to hard tissue, muscles, ligaments and tendons are affected. Muscles are blocked, spasmodic phenomena occur in them. The body tries to immobilize the affected area as much as possible in order to reduce pain - this leads to muscle congestion and muscle atrophy.
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
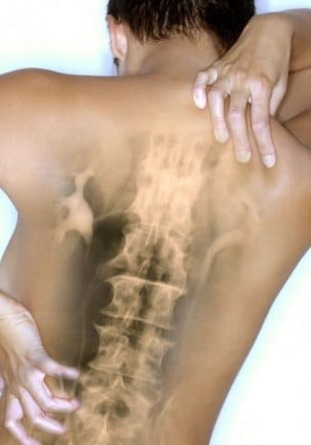
As already mentioned, at the stage of onset, thoracic osteochondrosis manifests itself weakly or does not manifest itself at all. As the pathology progresses, periodic pain appears between the shoulder blades: the symptoms intensify after physical activity or, on the contrary, after prolonged rest. Often the pain bothers patients in the morning after waking up and subsides within an hour. Sometimes the pain travels along the intercostal nerve, radiating to the chest when coughing, sneezing, or running.
Typical signs
At 2-3 stages, the most telling symptom of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is constant pain in the interscapular area. Chest pain is also quite typical: the sensations resemble an angina attack with coronary artery disease or heart failure.
The similarity of symptoms to heart disease is a fairly common cause of misdiagnosis. However, it is quite simple to distinguish pain in degenerative processes of the spine from cardiac symptoms: nitroglycerin and similar drugs that stop angina attacks, with osteochondrosis, in no way alleviate the patient's condition.
Other characteristic symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- Stiffness of the core muscles during deep breathing (back pain) - as if the body is pressed with a hoop;
- Dorsago - a sharp pain in the chest (so called “thoracic lumbago”);
- Goosebumps sensation and numbness in the hands (in the presence of radicular syndrome);
- Intercostal pain during walking and physical activity (intercostal neuralgia): with inflammation of nerve endings the pain becomes constant;
- Spasms in the thoracic back;
- Pain when raising arms, twisting torso, and breathing deeply.
The stages of the disease directly affect the intensity of symptoms. For patients therapeutically, it is important not to eliminate the pain with drugs and unconventional methods (analgesics, antispasmodics, various ointments, compresses and heating pads), but to go to the clinic and find the cause of thepain from a doctor. Self-treatment of osteochondrosis is rarely effective and in some cases even worsens the course of the disease.
Rare symptoms
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic area is often disguised as other pathologies, causing their symptoms. This complicates the diagnosis and is often the cause of inadequate treatment.
The atypical manifestations of the disease are very diverse:
- Signs of ischemia, heart attack, heart attack (ECG or other tests should be done for differential diagnosis);
- Pain reminiscent of breast disease in women: to exclude the presence of neoplasms, you must be examined by a mammologist;
- Pain resembling gastritis, colitis, stomach or intestinal ulcers, hepatitis - to exclude these diseases, a diagnosis is prescribed by a gastroenterologist;
- Pain in the paroxysmal girdle corresponding to renal colic or other diseases of the urinary system.
Urinary disorders and disorders of the reproductive system are also possible. Women suffer from anorgasmia, painful and heavy periods (menorrhagia) and sometimes infertility. Men suffer from erectile dysfunction. Doctors are not always able to find the true cause of these pathologies, and therefore the treatment of reproductive diseases does not give a positive dynamic.
Sometimes with osteochondrosis in the thoracic region, pressure spikes, toothaches and headaches, sleep disturbances, tinnitus are observed. Psycho-emotional disorders are not excluded - irritability, depression, tearing, anxiety.
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention
An external examination, palpation, and range of motion tests are performed to detect the disease. It is important to obtain detailed information from the patient about the duration of symptoms, their nature and concomitant manifestations of the disease.
The following procedures are prescribed:
- X-ray of the spine;
- MRI, CT and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (if necessary);
- Blood and urine tests;
- Myelography;
- ECG (to exclude cardiac pathologies).
Once the diagnosis is made, a treatment regimen is developed. There is no single protocol for the treatment of osteochondrosis: health procedures depend on the patient's condition, age, physical condition, and the state of the immune system.
The main objective of treatment is to minimize the consequences of degenerative processes in the cartilage tissue and to prevent the development of complications. Therapy is generally outpatient, with the exception of particularly severe clinical situations. Most of the time, conservative therapy is used.
Drugs
Medicines are prescribed only for severe pain syndrome and inflammatory processes. It is better to use drugs in the form of external ointments, less often tablets are prescribed, intramuscular or epidural injections.
Most types of topical medications:
- Analgesics;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Muscle relaxants and antispasmodics;
- vitamin complexes;
- steroids.
Experienced therapists will never offer purely drug therapy. Once the pain and inflammation have subsided, the drug is stopped.
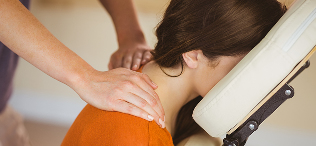
Physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage
These methods play a leading role in the treatment of degenerative diseases of the thoracic spine. These techniques eliminate pain, strengthen ligaments and muscles, restore and stimulate blood circulation, metabolic processes.
Popular physiotherapy methods:
- Magnetotherapy;
- Electro- and phonophoresis;
- Laser exposure;
- Amplipulse therapy;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- Paraffin applications;
- Kinesio recording;
- Mud therapy;
- Balneotherapy;
- Hypothermia;
- Hirudotherapy, treatment with bee venom.
The main benefit of physiotherapy is its safety. Procedures can be prescribed at any age, with almost any concomitant disease. A separate area of physiotherapy is reflexology (acupuncture). The method is effective, but requires the presence of a professional specialist.
Physiotherapy is an obligatory step in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis. Gymnastics strengthens the muscular apparatus, restores the normal anatomical position of vertebral structures, reduces pressure on nerve endings and prevents the development of protrusions and hernias of intervertebral discs.
Complex exercises should be performed regularly and for a long time - only in this case they will produce a noticeable therapeutic effect. Ideally, sessions should be conducted under the direction of an instructor, as any wrong movement can injure and cause pain.
Massage(manual and material effects) has the same therapeutic tasks as exercise therapy: pain reduction, improvement of blood flow, muscle strengthening. In addition to the impact with the hands of a specialist, they practice the use of massagers, applicators, orthopedic devices.
Radical treatment
Surgery for osteochondrosis of the breast in modern medical institutions is used in exceptional cases - when there is a real risk of pinching the spinal cord or with dangerous protrusions and hernias. Spine surgery is always an additional risk, so procedures are rarely performed and only by experienced surgeons.
Prevention
Prevention of disease is much easier than long-term (and sometimes lifelong) therapy. Alas, modern medicine cannot reverse degenerative processes, it can only minimize the consequences of pathology and eliminate acute symptoms.
For this reason, prevention of osteochondrosis should be approached from childhood. The development of the disease is hampered by: correct posture, a balanced diet, correct alternation of physical activity and rest, sleep on a comfortable bed. Timely diagnosis of the disease and strict implementation of the recommendations of the doctor play a positive role.

















































